Web site: www.w3.org/People/Berners-Lee/WorldWideWeb.html
Category: Network
Subcategory: Web browsers
Platform: NeXTSTEP
License: Public Domain
Interface: GUI
Wikipedia: WorldWideWeb
First release: December 25, 1994
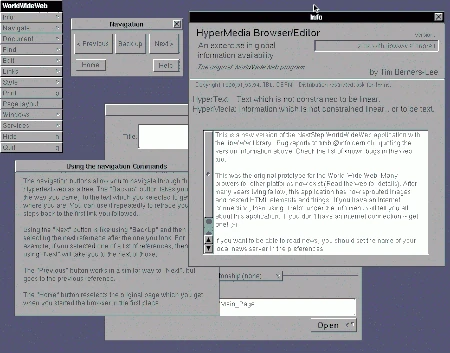
WorldWideWeb (later: Nexus) – the first web browser developed by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in the fall of 1990. It was written in the Objective-C programming language and run on the NeXTSTEP operating system. Later, WorldWideWeb was renamed Nexus to more clearly distinguish it from the World Wide Web.
The program supported the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), developed by Berners-Lee in 1989, as well as the widely used FTP protocol and provided access to news servers. The browser never achieved widespread adoption because it only ran on the NeXTSTEP environment, which, while very advanced at the time of its development, was not widely used.
On December 25, 1990, WorldWideWeb communicated for the first time with the first web server, also programmed by Berners-Lee, which was accessed via the domain info.cern.ch. Stylesheets were supported for formatting web pages. The browser also functioned as an editor for HTML documents, although only local documents could be edited. The prototype could not yet display graphics embedded in web pages; these opened in a separate window. WorldWideWeb was able to open all file types supported by NeXTSTEP.
In June 2021, Tim Berners-Lee auctioned an NFT of a signed copy of the source code for the equivalent of US$5.4 million through Sotheby’s. He intended to donate his share of the proceeds to charity.

I didnt expect it still exist in the wild
it does, but it is archived only, not in use any more